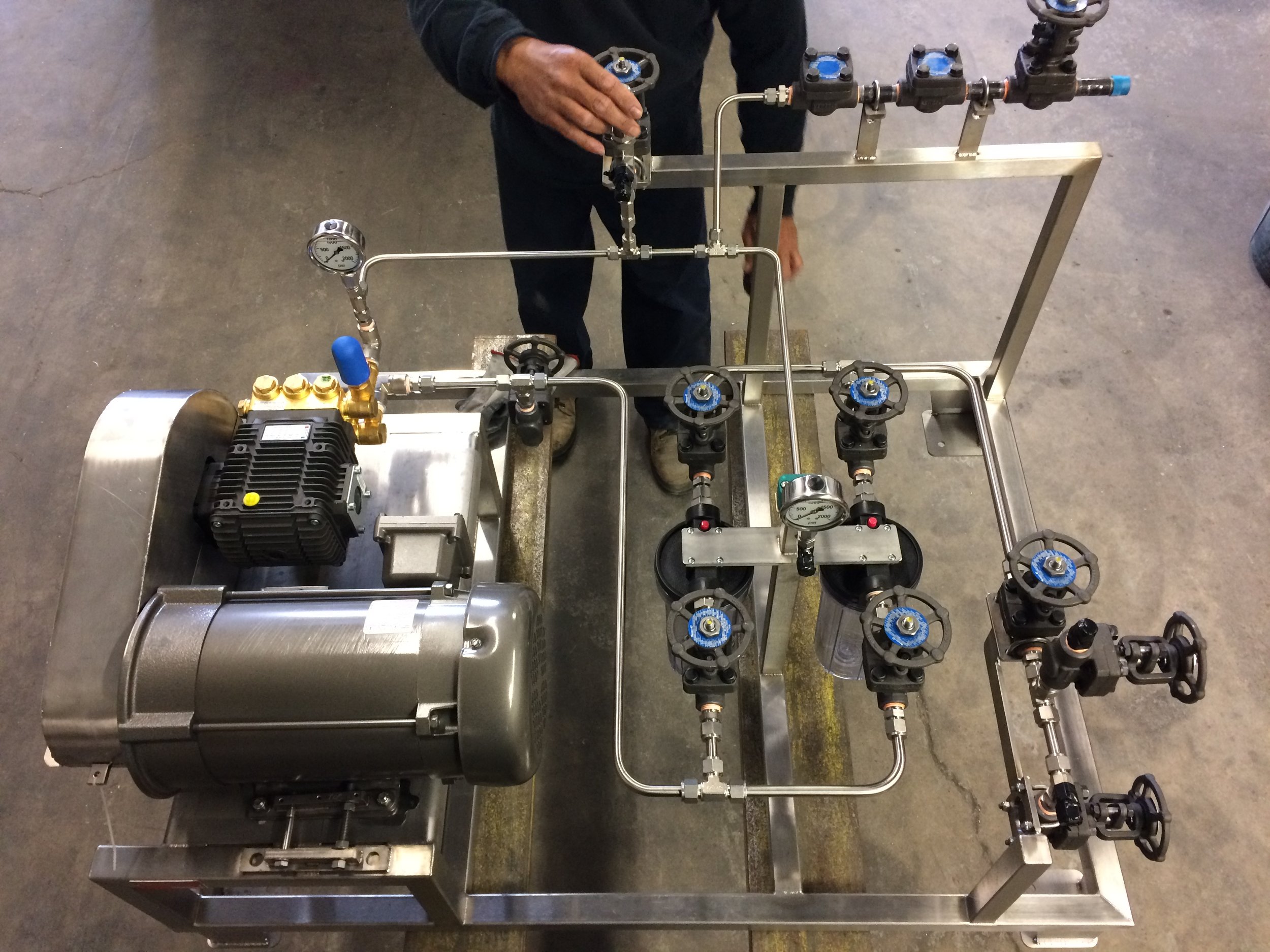
On Site Service
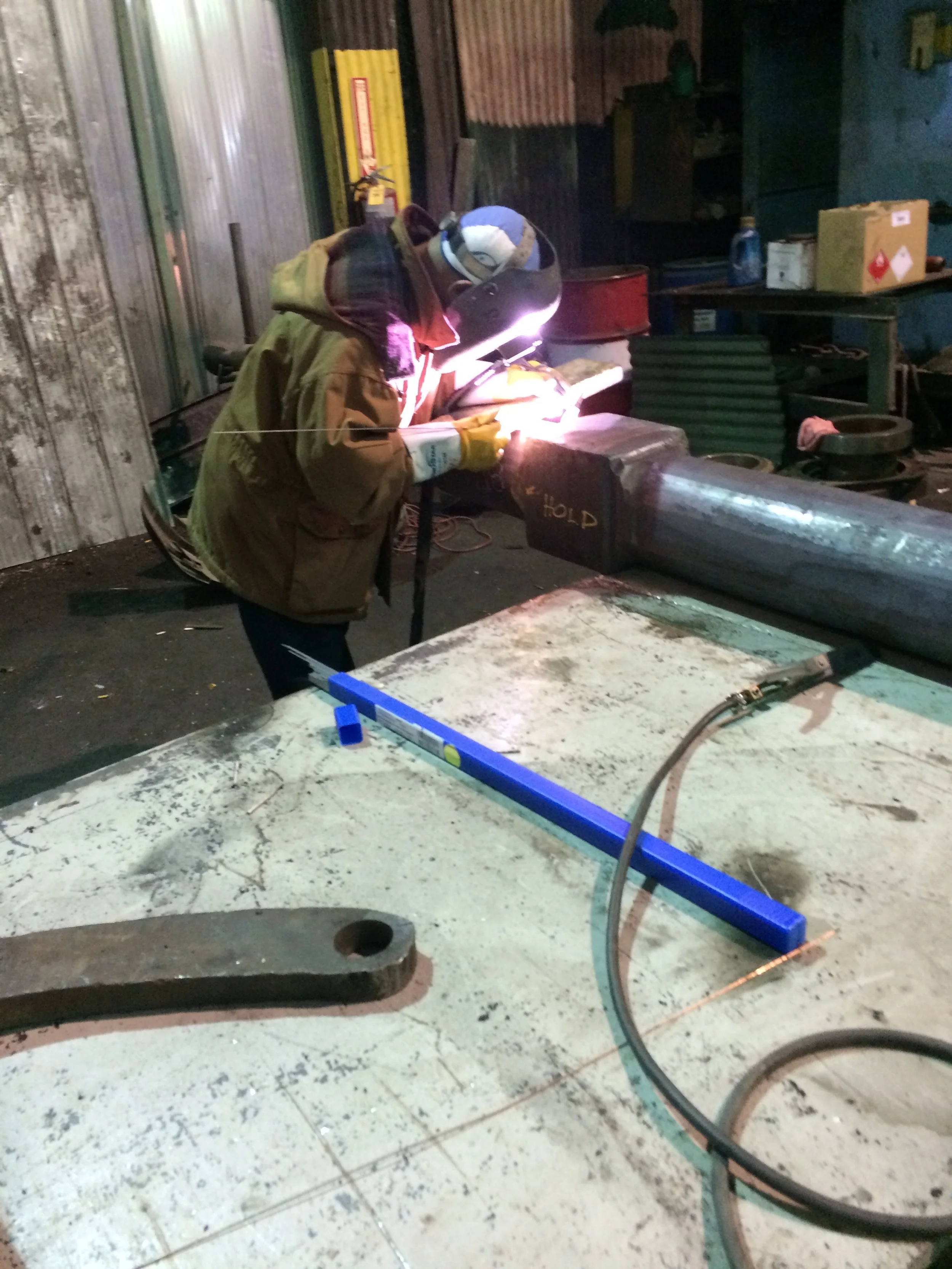
Installation
System setup: This includes physically installing the pump system in its designated location, securing it to a proper foundation, and connecting it to the fluid intake and output pipes.
Electrical and mechanical connections: The service connects the pump system to its power source, ensuring all electrical wiring is done correctly.
Alignment and lubrication: After initial installation, mechanics check and ensure the alignment between the pump and driver is correct. They also add the proper type and amount of lubricant to the bearing housings.
Testing and commissioning: Once assembled, the system is tested to confirm it is operating correctly, with no leaks and that it is moving the fluid at the expected rate.
Training
System Overview: A review of the specific pump system's design, its major components (pumps, motor, piping, controls), and their functions.
Normal Operation: Procedures for proper start-up, operation under various conditions, and shut-down.
Control System: Detailed description and operation of the control panel, including any automation, variable frequency drives (VFDs), and the importance of avoiding overrides.
Routine Maintenance: Instruction on daily/weekly checks, such as inspecting for leaks, unusual noises or vibrations, checking pressure gauges, and monitoring bearing temperatures and oil levels.
Safety Procedures: Emphasizing critical safety protocols, including lockout/tagout procedures and the safe handling of the pumped fluid.
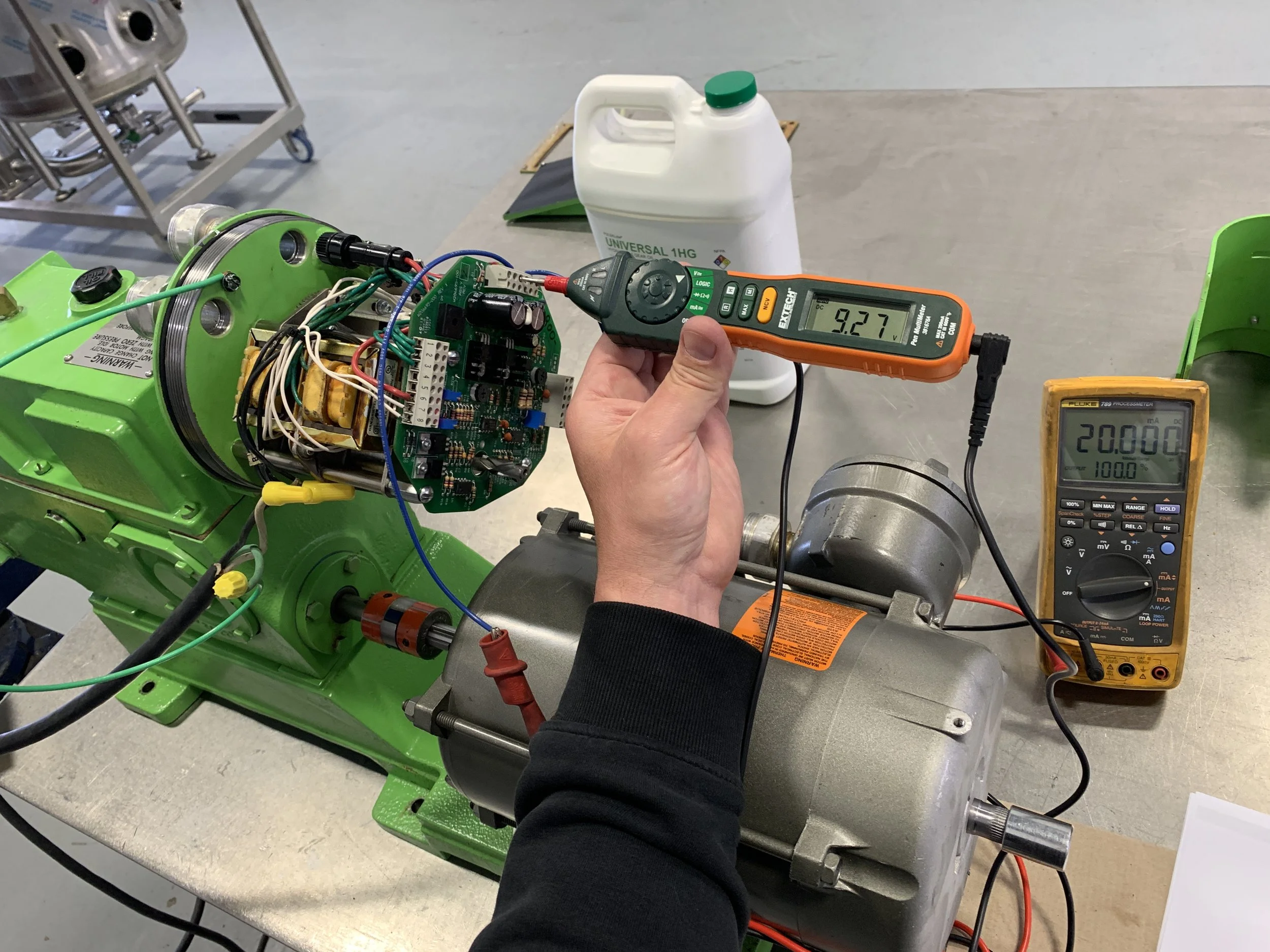
Basic Troubleshooting: Guidance on identifying common issues (e.g., cavitation, motor problems, seal failures) and the initial steps to address them before escalating to expert support.
Documentation: Reference to the complete system manual and any specific post-installation documents provided for future reference.
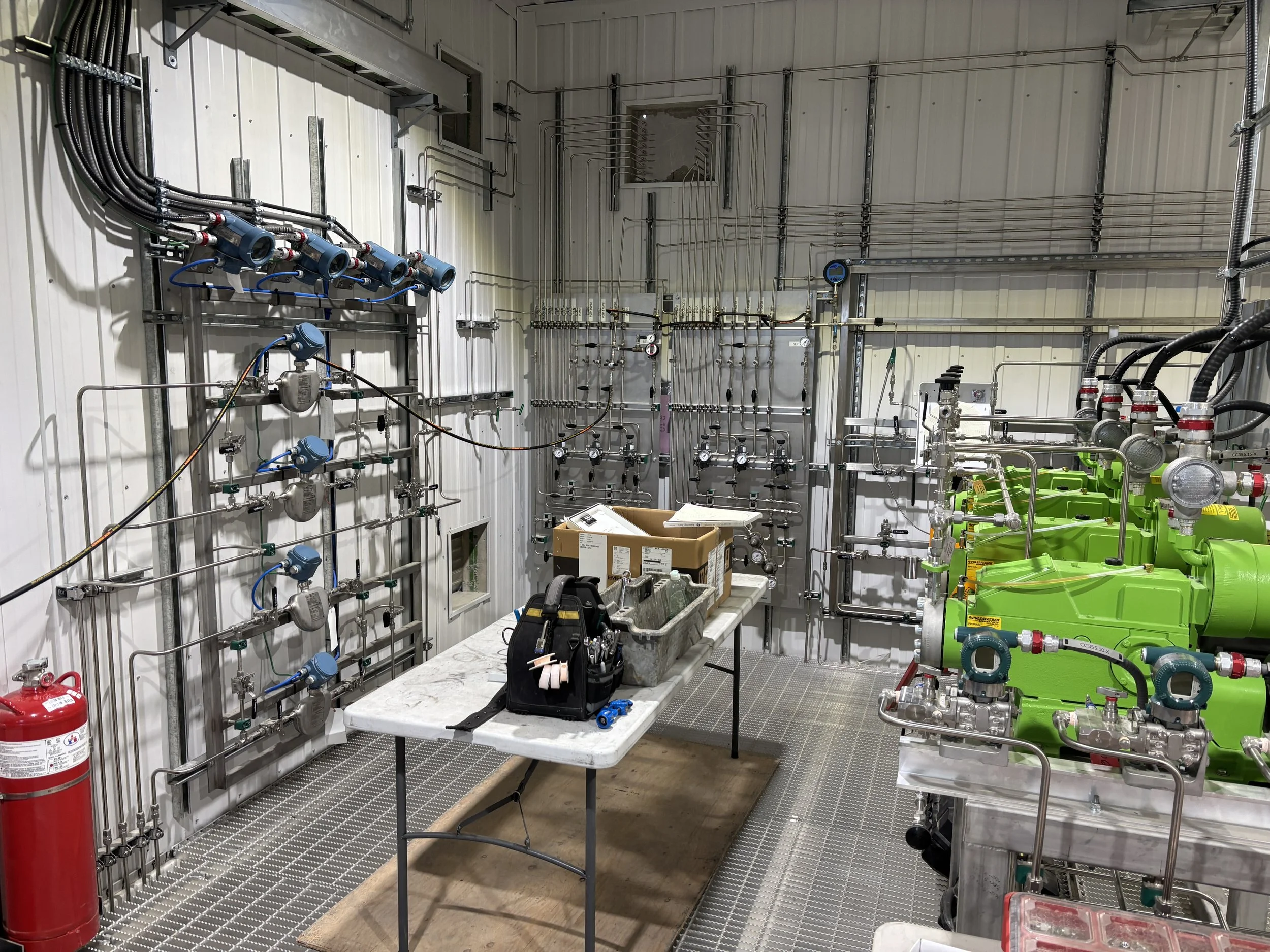
Maintenance
Visual inspections: Spotting leaks, abnormal noises, and vibrations is crucial for early detection of problems.
Performance monitoring: Verifying the pump's performance against its design specifications.
Part replacement: Replacing worn components like seals, gaskets, and impellers on a schedule to prevent failure.
Lubrication: Lubricating bearings and other joints according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
Cleaning: Cleaning strainers, filters, and impellers to maintain efficient flow rates.
Leak repair: Addressing leaks from seals, gaskets, or pipework.
Noise investigation: Diagnosing the source of unusual noises like clunking or cavitation.
Alignment checks: Adjusting motor alignment if it is a source of vibration.
Oil checks: Monitoring oil levels and condition.